In modern life, stress has become an almost inevitable companion. Everyday demands, deadlines, obligations and life changes often put us under pressure. And while we can't completely avoid stress, we can learn how to deal with it in a healthy and effective way. One of the ways we can beat stress is on our plate.
You know very well that food is fuel for our body, but you may not be aware of how much power a properly selected diet has when it comes to dealing with stress. That's exactly why we decided to present you this blog under the title "Let food be your ally against stress!"
Throughout this blog, we will explore the connection between food and stress. We will discover how certain foods can positively affect our mental health and emotional well-being. We will find out which foods act as natural anti-stress allies and how you can include them in your daily diet.
In addition to considering the benefits of certain foods, we will also explore how nutrition can affect energy levels, mood and ability to concentrate. We will share with you practical tips on how to change your eating habits and take steps to reduce stress in your everyday life.
In the next parts of this blog, we will discover recipes that can help you relax and enjoy delicious meals that protect your mental health at the same time. We will also deal with topics such as emotional overeating, mindful eating and an individual approach to nutrition in the context of stress.
The impact of nutrition on mental health
Nutrition plays a key role in maintaining our mental health and emotional stability. Our brains are extremely sensitive to the nutrients we ingest through food, and their correct balance can have a significant impact on our mood, cognitive function and ability to cope with stress.
A proper diet, rich in a variety of nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, can improve the neurotransmitters in the brain that are responsible for mood regulation. For example, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, nuts and flaxseed, help reduce inflammation in the brain and can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
In addition, foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can protect the brain from oxidative stress and damage to brain cells. In addition, the intake of adequate amounts of protein and complex carbohydrates can maintain stable blood sugar levels, preventing mood swings and emotional crises.
It is important to note that diet is not a magical solution to stress, but it is an important part of an overall approach to maintaining mental health. By combining proper nutrition with other stress management strategies, such as physical activity, meditation and good sleep, we can create a powerful ally in fighting stress and maintaining emotional stability.

Foods to reduce stress
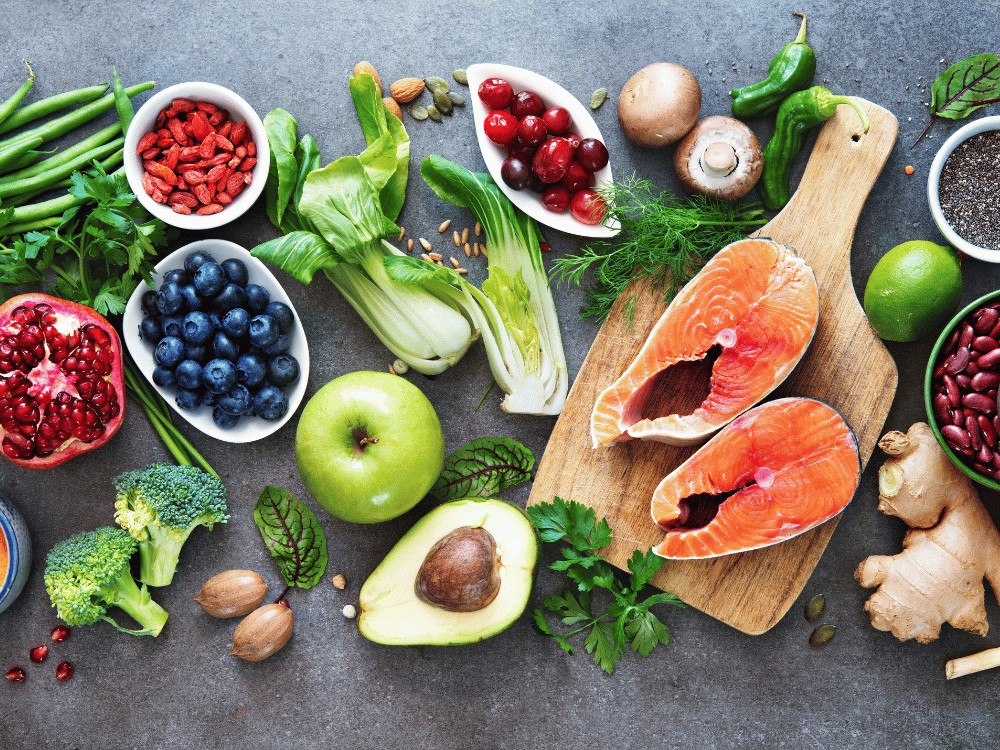
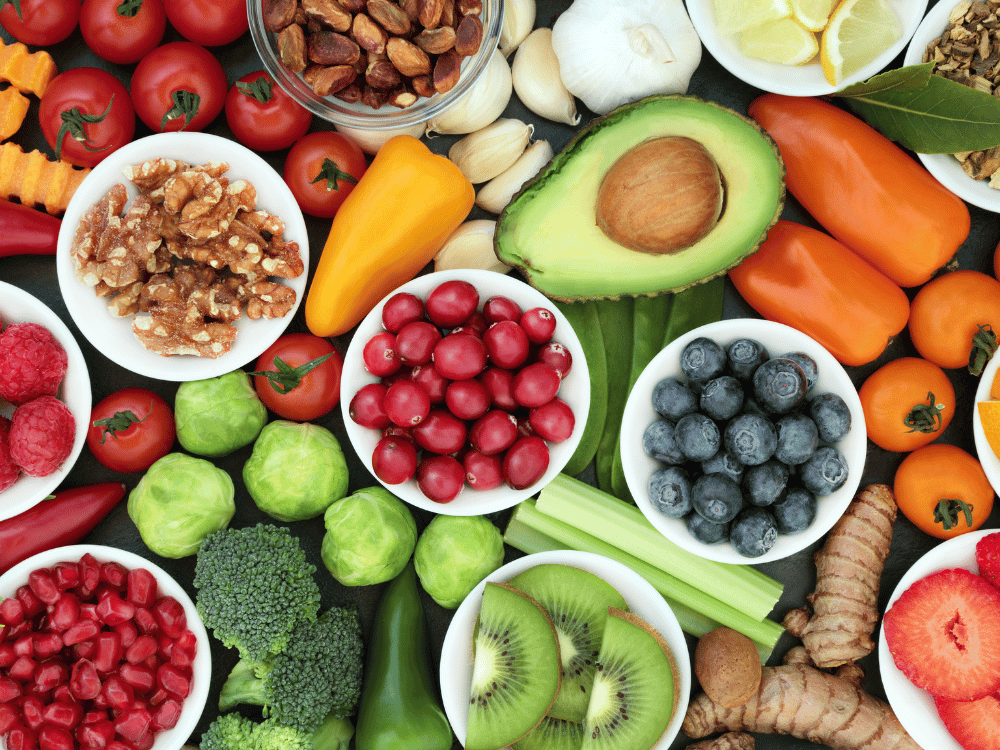
There are certain foods that can be considered natural allies in the fight against unpleasant conditions, such as dealing with stress and anxiety on a daily basis. We will analyze in detail seven such foods that are particularly useful for reducing stress and anxiety levels.
Tuna and Salmon: Omega-3 fatty acids
These marine fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce levels of inflammation in the brain, which is associated with stress and anxiety. Also, omega-3 fatty acids can improve the function of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which play a key role in mood regulation.
Almonds: Magnesium
Almonds are an excellent source of magnesium, a mineral that plays a key role in stress regulation. Magnesium helps relax muscles and nerves, reducing physical tension associated with stress. Also, this mineral supports the production of neurotransmitters that affect mood. Daily consumption of almonds can help maintain a stable level of magnesium in the body.
Oats: Tryptophan and Serotonin
Oats are rich in the amino acid tryptophan, which is a precursor to serotonin, known as the "hormone of happiness." Serotonin plays a key role in regulating mood and reducing anxiety. Eating oat products, such as oatmeal or oatmeal cookies, can help increase serotonin levels in the brain and reduce stress.
Kale: Folic acid
Kale is extremely rich in folic acid, which is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Folic acid deficiency can lead to increased anxiety and fatigue. Including kale in your diet can help maintain optimal folic acid levels and reduce stress.
Avocado: Rich in potassium and vitamin B6
Avocados are an excellent source of potassium, a mineral that can help regulate blood pressure and reduce tension. Also, avocados contain vitamin B6, which is necessary for the production of neurotransmitters, including serotonin. Regular consumption of avocados can support emotional stability and relieve stress.
Forest fruits: Anthocyanins and vitamin C
Berries such as blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are rich in antioxidants, including anthocyanins and vitamin C. These antioxidants help neutralize free radicals that can cause oxidative stress in the brain. Regular consumption of berries can support mental clarity and reduce stress.
Spinach: Magnesium and folic acid
Spinach is an excellent source of magnesium and folic acid. Magnesium helps relax muscles and the nervous system, while folic acid contributes to the production of neurotransmitters. This combination can help reduce physical and emotional tension. Including spinach in your diet can contribute to your sense of calm and emotional balance.
It's important to note that nutrition should be part of an overall approach to maintaining mental health, along with physical activity, good hydration and other stress management strategies. Including these foods in your diet can be a step towards reducing stress and improving emotional stability.

How can nutrition affect energy levels, mood and ability to concentrate?
Proper nutrition can act as a powerful tool for maintaining optimal mental and physical well-being.
First, energy level is directly related to nutrient intake. Food is the source of fuel for our body, and carbohydrates are key to providing quick and sustained energy. Eating complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, vegetables and legumes, allows for a gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream, keeping blood sugar levels stable and preventing swings that can cause fatigue.
Second, diet has a direct relationship with mood. Foods rich in nutrients like vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids and amino acids, especially tryptophan, can help regulate brain chemicals that affect mood. For example, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and nuts, can improve the production of serotonin, the happy hormone.
Third, diet can affect concentration and cognitive function. The brain is an organ that requires an abundance of oxygen and nutrients, so a diet that promotes healthy blood vessels and blood flow to the brain can improve cognitive performance. Antioxidants from fruits and vegetables, as well as flavonoids and polyphenols, have been shown to be beneficial in maintaining optimal mental health and function.
Stabilizing blood sugar for less anxiety
When blood sugar levels fluctuate between extremes, such as sudden spikes after eating fast food or sudden drops between meals, the body can react to such fluctuations by causing feelings of anxiety and nervousness.
Eating right can help keep your blood sugar levels stable.
The key is to consume complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, vegetables and legumes, which are slowly broken down in the body and release glucose gradually. This gradual intake of energy helps prevent sudden spikes and drops in sugar levels.
It is also important to avoid foods high in simple sugars, such as sodas, sweets and fast food, as these products often cause rapid changes in blood sugar levels. These changes can cause symptoms such as tremors, nervousness and tension, which can contribute to feelings of anxiety.
Protein and healthy fats also play a key role in stabilizing blood sugar levels. Adding protein and healthy fats to meals helps slow the absorption of sugar and provides a longer-lasting source of energy. For example, the intake of nuts, avocados and fatty fish can be beneficial for maintaining blood sugar stability.
In addition, regular meals are an important factor in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Skipping meals can cause your sugar levels to drop and cause anxiety. Planning meals at regular intervals ensures that the body has a constant source of fuel to function.

A versatile approach to nutrition and Mindful Eating
Both concepts emphasize awareness and attention to the food we eat, which can have a profound effect on our emotional state.
A versatile approach to nutrition implies variety in the diet, including different types of foods and nutritional ingredients. This approach ensures that the body receives all the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning. A lack of certain vitamins or minerals can contribute to stress and poor mental health, so a varied diet plays a key role in maintaining balance.
Mindful eating focuses on being present in the moment during a meal. This includes focusing attention on the smell, taste, texture and sensations that food provides. Through this approach, people become aware of satiety signals, thereby reducing overeating and emotional overeating, which are often associated with stress.
Mindful eating also helps identify emotional eating. Many people turn to food as a way to cope with stress and negative emotional states. Practicing mindful eating allows us to recognize these patterns and focus on healthier ways of dealing with stress, instead of turning to unhealthy meals.
In essence, a holistic approach to nutrition and mindful eating together promote awareness of how food affects our body and mind. This deeper level of attention to nutrition can help reduce stress by empowering us to make better food decisions, better understand our emotional reactions to food, and better control our eating, all of which contribute to improved mental health.
Nutrition and mental health - A personalized approach
Diet and mental health are often linked, but it's important to understand that there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Individual needs and reactions to food vary, and research in this field allows for the development of personalized approaches to manage stress through nutrition.
One of the key factors in the development of personalized approaches is genetics. Genetic variation plays a role in how our body metabolizes nutrients and how it reacts to certain foods. Research in the field of nutrigenetics provides insight into genetic predispositions that can affect our susceptibility to stress and how certain nutrients can affect our mental health.
Also, research has shown that individual food preferences and allergies play a significant role in mental well-being. People who have allergies or intolerances to certain food ingredients may experience increased anxiety or other stress symptoms after consuming those foods.
Methods such as nutrigenomics and food intolerance testing enable personalization of nutrition to meet individual needs and reduce stress. For example, a person with a genetic predisposition to reduce serotonin production may benefit from foods rich in tryptophan, a serotonin precursor. On the other hand, a person with lactose intolerance may have reduced stress by avoiding dairy products.
Research in the field of nutrition and mental health enables the development of personalized approaches that take into account genetic, individual and metabolic factors. This helps people better understand how food affects their mental well-being and allows them to develop a diet tailored to their needs, which can significantly contribute to reducing stress and improving mental health.
Let food become your ally in the fight against stress. We believe that after this information, you are ready for a journey that will teach you how to take care of your body and mind through the right food choices. Good luck and enjoy the process!