Lately, dietary needs and choices have become a central topic of conversation. People are more and more aware of the impact of food on their body and health. Two popular diets that have gained attention are the gluten-free diet and the paleo diet. Both claim to offer numerous health benefits, but there are significant differences between them.
In this article, I will help you understand what each of these diets entails, their pros and cons.

Gluten-free diet
What is gluten?
Gluten is a protein found in some grains, including wheat, barley and rye. It consists of two proteins, glutenin and gliadin, which combine with water to form an elastic network that gives the dough its strength and elasticity. This is why gluten is an important ingredient in the production of bread and other baked goods.
However, some people have developed gluten intolerance. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease in which the consumption of gluten triggers an immune response that damages the intestines. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhoea, bloating and fatigue, and can damage the intestinal villi, making it difficult to absorb nutrients. Also, some people may have gluten sensitivity, which means they experience symptoms after consuming gluten, but do not have celiac disease.
Because of this, many people choose to eliminate gluten from their diet. There are many gluten-free products available on the market, including bread, pasta and pastries, which are made from alternative flours such as corn, rice, potato and almonds. However, it is important to be careful when buying processed products, as some may contain traces of gluten or be contaminated with gluten during production.
Who is the gluten-free diet for?
The gluten-free diet is intended for people with celiac disease, wheat allergy, or gluten sensitivity.
Celiac disease
This is an autoimmune disease where the consumption of gluten triggers an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine. People with celiac disease must avoid gluten completely to prevent serious intestinal damage and other complications.
Wheat allergy
This is an allergic reaction to proteins found in wheat, including but not limited to gluten. People with a wheat allergy must avoid wheat, but may be able to tolerate gluten from other sources, such as barley or rye.
Gluten sensitivity
This is a condition where people experience symptoms after consuming gluten, but do not have celiac disease or a wheat allergy. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, headache, and fatigue.
A gluten-free diet may also be beneficial for people with other health conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, although the evidence for this is still inconclusive.
However, it is important to note that a gluten-free diet is not necessarily healthier for the general population. Gluten itself is not harmful to most people, and many gluten-free products can be less nutritious and contain more calories and added sugar than their gluten-free equivalents. Therefore, unless you have a medical reason to avoid gluten, it is not advisable to switch to a gluten-free diet just to improve your health.
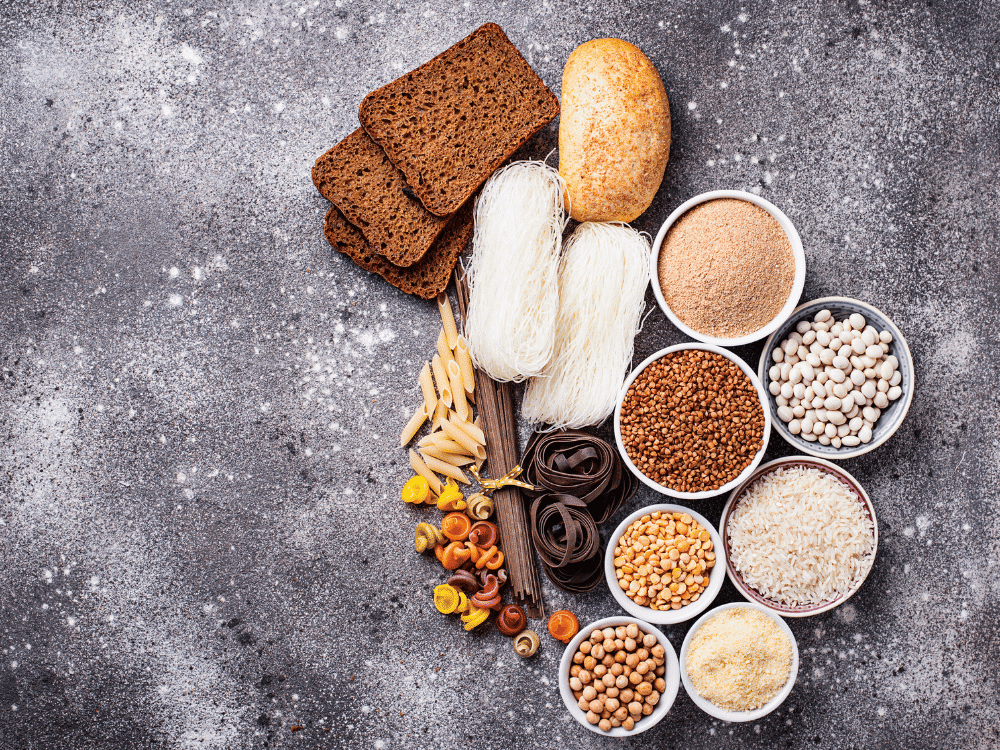

Advantages and disadvantages of a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet is essential for people with celiac disease, wheat allergy, or gluten sensitivity because it can help manage symptoms and prevent intestinal damage or other complications. However, for people who do not have these medical problems, the pros and cons of a gluten-free diet may be less clear.
The benefits of a gluten-free diet
Symptom management: For people with celiac disease, wheat allergy, or gluten sensitivity, a gluten-free diet can help manage symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, headaches, and fatigue.
Prevention of complications: For people with celiac disease, gluten consumption can lead to damage to the intestinal villi, which can make it difficult to absorb nutrients and lead to other complications such as anemia, osteoporosis, and an increased risk of cancer. A gluten-free diet can help prevent these complications.
Improving digestion: Some people without a diagnosis of celiac disease, wheat allergy, or gluten sensitivity report improved digestion after switching to a gluten-free diet.
Weight loss: A gluten-free diet can help many people lose weight if they are used to consuming a large amount of high-calorie pasta during the day. In one of our previous texts, we also covered the topic gluten-free tolerance and weight loss and in this text you can find an example of a menu for people who avoid gluten.
Disadvantages of a gluten-free diet:
Less nutrients: Many foods that contain gluten, such as fortified cereals and breads, are important sources of B vitamins, iron, fiber and other nutrients. Gluten-free alternatives often contain less of these nutrients.
More calories: Many gluten-free products contain more calories, sugar and fat than their gluten-free counterparts.
More difficult meal planning: Finding gluten-free products can be a challenge, especially when eating out or traveling.
Higher costs: Gluten-free products are often more expensive than products that contain gluten.
In summary, a gluten-free diet can have numerous benefits for people with celiac disease, wheat allergy, or gluten sensitivity. However, for people who do not have these medical problems, a gluten-free diet can present many challenges.
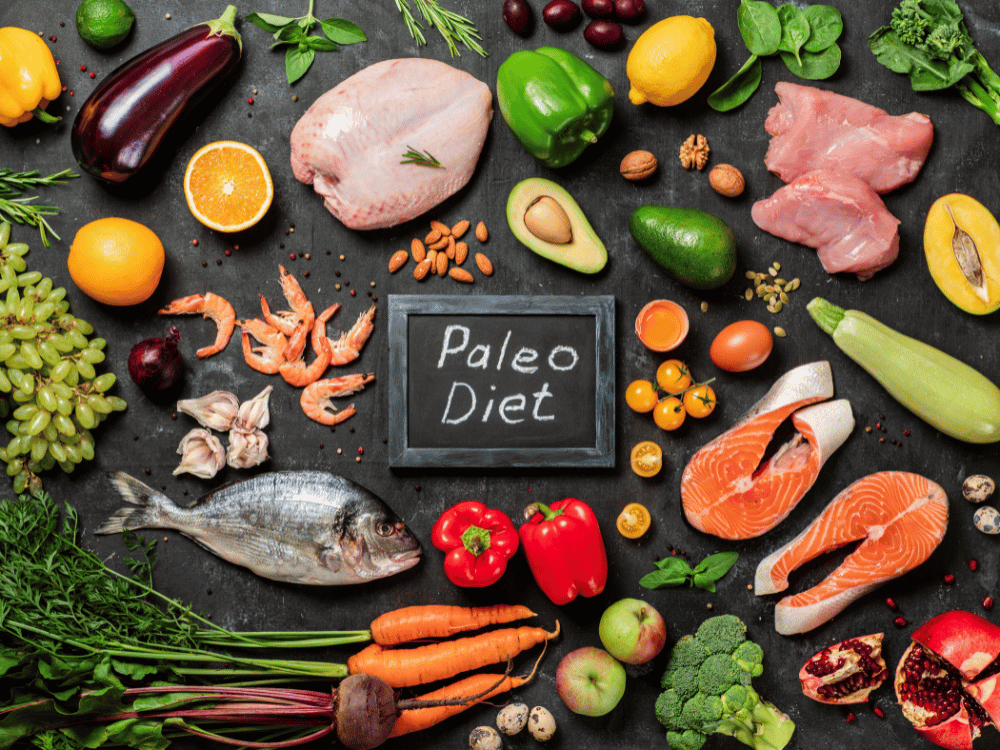

Paleo diet
What is the Paleo diet?
Paleo diet, also known as the "prehistoric diet" or the "ancestral diet," is a way of eating that tries to mimic the diet of our Paleolithic ancestors, who lived about 2.5 million to 10,000 years ago. This was before agriculture began, so the paleo diet focuses on foods that were available through hunting and gathering, such as meat, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
The Paleo diet excludes many foods that have become common with the development of agriculture and industrialization, such as grains, dairy products, refined sugars, processed oils, and other processed foods.
Proponents of the paleo diet claim that this is the way the human body evolved and that eating more whole, unprocessed foods can help prevent chronic disease, improve fitness, and lose weight.
Critics of the paleo diet, however, point out that it is difficult to accurately recreate the diet of our ancestors and that the modern environment and health challenges require a modern approach to nutrition.
Who is the paleo diet for?
The Paleo diet is intended for anyone who wants to eat in a way that mimics the diet of our Paleolithic ancestors. This may include people who:
They want to lose weight: The Paleo diet emphasizes eating whole, unprocessed foods that are typically lower in calories and more nutrient-dense than the processed foods that many people tend to eat.
They are trying to improve their health: Proponents of the paleo diet claim that it can help prevent chronic diseases, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Suffer from autoimmune diseases: Some people believe that the paleo diet can help manage the symptoms of autoimmune diseases, although the evidence for this is still limited.
They are looking for a simple, unprocessed way of eating: The Paleo diet excludes most processed foods, which can be appealing to those looking for a "cleaner" or "natural" way of eating.
However, it is important to note that the paleo diet can be restrictive and is not suitable for everyone. For example, it excludes all grains, dairy products and legumes, which are an important part of many people's diets. It can also be difficult to follow a paleo diet if you don't have the time or resources to prepare all your meals at home, as most processed foods are not allowed.
As with any diet, before starting a paleo diet, you should consult with a health care professional to make sure it's the right choice for you.

Advantages and disadvantages of the paleo diet
Benefits of the paleo diet
Emphasis on whole foods: The Paleo diet promotes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods, which are usually more nutritious and lower in calories than processed foods.
Avoiding processed foods: The Paleo diet excludes processed foods that often contain unhealthy fats, too much salt, and added sugars.
Increased fiber intake: Fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds are the main part of the paleo diet, which means that most people will have an increased fiber intake.
Improved insulin sensitivity: Eating fewer processed carbohydrates and more fiber and healthy fats can help improve insulin sensitivity.
Weight loss: Many people have also noticed weight loss on the paleo diet, although this is not the main goal of the diet.
Disadvantages of the paleo diet
Restrictiveness: The Paleo diet excludes many food groups, including grains, dairy products, legumes, and processed foods. This can make it difficult to stick to the diet long-term and can also increase the risk of certain nutrient deficiencies.
Higher costs: Eating more meat, fish, fruits and vegetables can be more expensive than eating more grains and processed foods.
Difficult to follow for vegetarians and vegans: The Paleo diet emphasizes the consumption of meat and fish, which can be problematic for vegetarians and vegans.
Possible nutrient deficiency: Avoiding grains, dairy products, and legumes can lead to deficiencies in nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins.
High intake of red meat: Some experts are concerned that the Paleo diet may encourage excessive consumption of red meat, which may be linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic diseases.
As with any diet, it is important to consider individual needs and goals before starting a paleo diet. While the paleo diet may have some benefits, it also has potential drawbacks that may make it unsuitable for some people.
Conclusion
Gluten-free and paleo diets have some similarities, but also key differences. Both diets exclude gluten, which can be beneficial for people with celiac disease, wheat allergy or gluten sensitivity. However, the paleo diet is more restrictive, also excluding dairy products, legumes and all processed foods.
Both gluten-free and paleo diets can have benefits for certain people, but they also carry risks and can be difficult to follow long-term. It is important to consider individual needs, goals and medical concerns before starting any regimen.
It's also helpful to talk to a health care professional or nutritionist who can help plan a balanced diet that will provide all the nutrients you need.